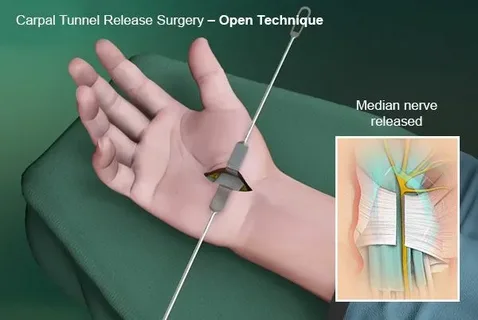
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes compressed at the wrist. While many cases can be managed with non-surgical treatments, some patients may require carpal tunnel surgery. Understanding when surgery is necessary and what to expect can help patients make informed decisions.
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) develops when the carpal tunnel—a narrow passageway in the wrist—places pressure on the median nerve. This pressure can cause symptoms such as:
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers
- Weakness in hand grip
- Pain in the wrist or forearm
Early intervention often includes wrist splints, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy. However, if these measures fail, surgery may be the next step.
When Carpal Tunnel Surgery is Needed
Carpal tunnel surgery: when it’s needed and what patients should expect typically arises in the following scenarios:
- Persistent Symptoms: If numbness, tingling, or pain continues for several months despite conservative treatment.
- Muscle Weakness: When patients notice a loss of grip strength or muscle wasting at the base of the thumb.
- Severe Nerve Compression: Confirmed through nerve conduction studies, indicating that prolonged compression could cause permanent nerve damage.
Surgery is considered a safe and effective option for relieving pressure on the median nerve and improving hand function.
Types of Carpal Tunnel Surgery
There are two main types of carpal tunnel surgery:
- Open Release Surgery: The surgeon makes a small incision in the wrist to cut the ligament pressing on the median nerve.
- Endoscopic Surgery: A less invasive procedure using a tiny camera and instruments to release the ligament through smaller incisions.
Your doctor will recommend the most appropriate method based on the severity of your condition and personal health factors.
What Patients Should Expect After Surgery
Understanding carpal tunnel surgery: when it’s needed and what patients should expect helps reduce anxiety and ensures better recovery. After the procedure, patients can expect:
- Pain and Swelling: Mild discomfort and swelling are common but manageable with medications.
- Wound Care: Keeping the incision clean and dry is essential to prevent infection.
- Rehabilitation: Hand exercises and physical therapy may be recommended to restore strength and flexibility.
- Recovery Timeline: Most patients regain normal hand function within 4 to 6 weeks, though full recovery can take several months.
Conclusion
Carpal tunnel surgery: when it’s needed and what patients should expect is a vital consideration for those suffering from severe or persistent carpal tunnel syndrome. By knowing the symptoms, understanding surgical options, and following post-operative care instructions, patients can achieve relief and restore hand function. Early consultation with a qualified healthcare provider is key to determining the right timing for surgery and ensuring optimal outcomes.